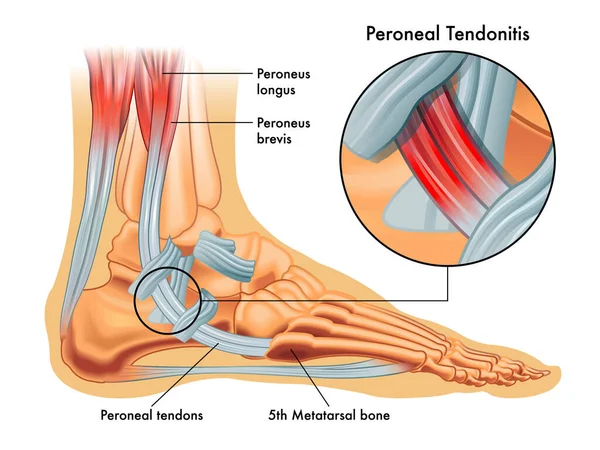
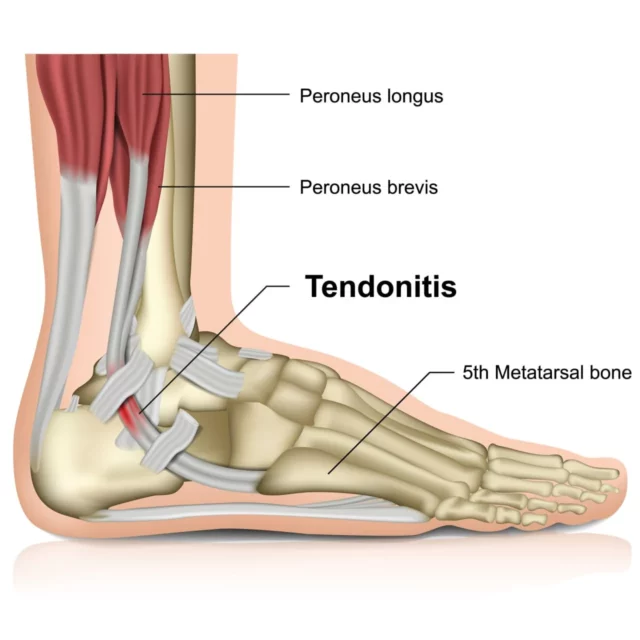
Experiencing pain and swelling on the side of your ankle could indicate a peroneal tendon injury. This tendon is crucial for stabilizing the foot and ankle, preventing abnormal or excessive movements that could lead to sprains or dislocations.
Due to repetitive and forceful movements, direct trauma, or improper posture, the peroneal tendon can become damaged or inflamed, leading to chronic pain and ankle instability. While acute injuries can often be resolved with at-home care, inadequate treatment can turn a minor problem into a long-lasting, impactful condition. Complicating the diagnosis is the fact that peroneal tendon injuries are common yet often not recognized, with a 40% misdiagnosis rate.
At NextPain Care, we can help you through each stage, from diagnosis to pain management. Let’s explore how below.
Understanding Peroneal Tendon Anatomy
Tendons are strong bands of connective tissue that connect muscles to bones. The peroneal tendon, composed of two separate tendons, connects structures in the foot, providing stability while bearing weight and protecting the ankle from injuries.
Composed of two primary tendons, the peroneal system works together to control foot movement.
- Peroneus brevis: This tendon connects the lower leg bone (fibula) to the outside of the foot.
- Peroneus longus: Originating from the fibula, this tendon runs along the outer ankle, under the foot, and attaches to the inside of the foot arch.
Conditions affecting the peroneal tendon, such as tendonitis and dislocations, are not uncommon, especially among athletes. It has been observed that 25-77% of patients with chronic lateral ankle instability have some type of peroneal tendon injury. Among those with peroneal tendon injuries, 10% experience major complications, such as continued symptoms and chronic pain.
Risk Factors And Causes Of Peroneal Tendon Pain
Despite its common occurrence, peroneal tendon pain is often under-recognized and misdiagnosed, leading to inadequate treatment and ongoing complications. Accurate diagnosis begins with identifying the risk factors and causes.
Risk Factors for Peroneal Tendon Injuries
Certain factors increase the risk of peroneal tendon injuries, including:
- Age over 40
- Lack of stretching before exercise
- History of tendon injuries
- Chronic conditions like diabetes
- Musculoskeletal conditions such as osteoarthritis or rheumatoid arthritis
- Obesity or being overweight
- Tight tendons or high foot arches
- Smoking
- Wearing unsupportive footwear
Common Causes of Peroneal Tendon Pain
Overuse and Repetitive Ankle Motion Due to Sports
Certain activities and sports place undue pressure on the peroneal tendons, causing them to become inflamed, irritated, or even torn. Those at greater risk include:
- Runners: Running on sloped streets or uneven terrain can cause the foot to roll outward, increasing friction and tension between the tendon and bone.
- Marathoners: Long-distance runners typically suffer from peroneal tendonitis due to repetitive motion.
- High-impact sports participants: Sports involving quick, forceful movements of the foot, jumping, and squatting can overstretch and cause micro-tears in the tendon.
Working with a specialized coach can help prevent foot and ankle injuries, which are common among runners and other athletes.
Sudden Trauma
Traumatic injuries, such as those from vehicle collisions, can lead to fractures and dislocations of the foot, pulling on the peroneus tendon and causing pain. Non-contact injuries, resulting from abnormal ankle movements or landing awkwardly, are also common. These include:
- Inversion of the ankle
- Excessive or forceful dorsiflexion (raising your toes toward your shin)
- Ankle sprains
- Recurrent dislocation of the peroneal tendons
Poor Form While Training
Athletes’ form during training can significantly influence the risk of peroneal tendon injuries. Misalignment during workouts places undue stress on foot and ankle tendons, especially during high-impact activities like running or jumping. Over time, this can lead to micro-tears and peroneal tendon pain. Ensuring correct postural alignment during training is beneficial for performance and injury prevention.
Increase In Activities Such As Jumping, Running, Or Walking
A sudden increase in high-impact activities can strain the peroneal tendon excessively, leading to progressive tendon damage. Starting high-intensity activities without adequate training means the ankle and foot muscles are not well-conditioned, making injuries like strains, sprains, and over-stretching of the tendons more likely. Working with a trainer can help progressively increase workout intensity while preventing injuries.
High Foot Arches
High arches (pes cavus) significantly contribute to peroneal tendon pain and injury likelihood, due to increased pressure on the outer side of the foot. The peroneal tendons must work harder to stabilize the foot during walking or running, leading to inflammation or injuries over time. Healthcare providers may recommend orthotics to correct gait and alleviate excessive pressure on the peroneal tendon.
Tight Calves
The strength and flexibility of calf muscles are important in diagnosing peroneal tendon pain since the peroneal tendons attach to the base of the leg. Tight calf muscles can transmit greater tension and load to the tendons, causing strain, inflammation, and damage over time. Flexibility and mobility exercises for the calves can help address this risk factor.
Possible Conditions Associated with Peroneal Tendon Pain
Peroneal tendon pain can be linked to various conditions affecting different parts of the foot. The most common conditions include tendinopathy, dislocations, tears, and plantar fasciitis. Let’s explore these in more detail.
Peroneal Tendinopathy (Tendonitis)
Tendonitis occurs when the tendon becomes inflamed, affecting one or both peroneal tendons. Common causes are overuse and sudden trauma, such as ankle sprains or direct injury. The inflammation leads to fluid build-up around the injury site, resulting in swelling, stiffness, and pain, typically localized along the outer area of the ankle and foot.
Peroneal Dislocation and Subluxation
A dislocation happens when the tendon completely snaps out of position, while subluxation is a partial dislocation. Dislocations can result from abnormalities in the foot’s shape, causing abnormal tendon movement, or from direct trauma, such as fractures in the ankle or foot that pull the tendon away from its normal position.
Peroneal subluxation causes pain, snapping sensations when moving the ankle, instability, and weakness. Repeated subluxation increases the risk of further injuries, such as tears and ruptures.
Peroneal Tendon Tears
Tendon tears can be caused by repetitive activity or trauma (acute tears) and degenerative changes from age or overuse (degenerative tears, or tendinosis). Symptoms include pain on the outside of the ankle, swelling, weakness, instability, and difficulty bearing weight. You may also notice changes in foot shape, such as an increased arch height. Severe tendon damage can lead to a complete tear.
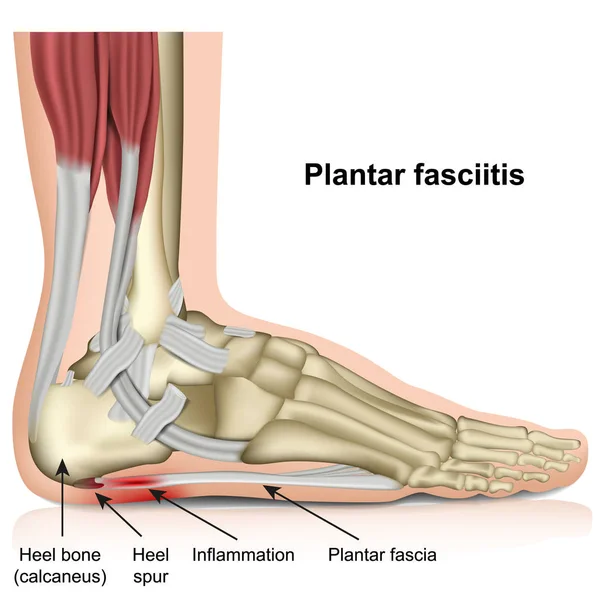
Plantar Fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis, a common cause of heel pain, can also contribute to peroneal tendon issues. This condition arises when the plantar fascia, a tissue band connecting your heel to your toes and stabilizing the foot’s arch, develops small tears due to excessive tension or stress.
Risk factors for plantar fasciitis include obesity, prolonged standing, and tight Achilles tendons, all of which strain the plantar fascia. Damage or irritation of the fascia leads to symptoms such as heel pain and instability. These symptoms, along with uneven weight distribution and altered gait, can increase strain on the peroneal tendons, causing pain to spread across the side of the foot.
Peroneal Tendon Pain Diagnosis
If you have a mild ankle sprain, self-care, activity modification, and rest may be sufficient for recovery. However, if the pain is severe or persistent, interfering with daily activities, it is important to seek medical advice.
You should contact your healthcare provider if:
- You are unable to walk.
- You cannot put weight on your foot or ankle.
- You cannot rotate your ankle.
- You experience popping sensations.
- The pain and swelling progressively worsen.
Isolated injuries to the peroneal tendons are rare and often misdiagnosed, as the symptoms can overlap with those of sprains, fractures, or arthritis. However, your doctor can use several diagnostic tools to identify the source of your pain:
- Physical Examination: This includes palpation of the ankle and foot, as well as tests to evaluate the range of motion in the joint.
- Review of Symptoms and Medical History: Your doctor will assess your symptoms and medical history to understand the context of your pain.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRI, and CT scans can help rule out conditions such as fractures, torn cartilage, and osteoarthritis.
Accurate diagnosis is crucial for appropriate treatment and recovery, ensuring that underlying issues are properly addressed.
Common Treatment Options for Peroneal Tendon Pain
In many cases, peroneal tendon pain can be effectively managed through at-home care and conservative treatments. These options include:
RICE Method
Rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE) can help reduce pressure on the ankle, decrease swelling, and ease pain while the injury heals. However, there are some controversies regarding its efficiency, particularly as it may reduce blood circulation around the injured area.
Medication
Over-the-counter painkillers, topical creams, and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can temporarily reduce pain and inflammation. Corticosteroid injections may also be considered for longer-lasting pain.
Bracing
Using a brace can reduce pressure on the ankle and foot, stabilizing the joint to prevent further injury, especially during activities like running or jumping. In some cases, a soft cast may be recommended to immobilize the foot while it heals.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy can help strengthen and improve the flexibility of the muscles in the foot and ankle, supporting the healing process and preventing further injury.
Surgery
If peroneal tendon pain does not improve with conservative measures, surgery may be recommended. Surgical interventions aim to remove or clean the layers of tendon tissues affected by inflammation. Like all invasive procedures, surgery carries inherent risks and should be carefully considered.
Preventive Measures
To prevent peroneal tendon pain, consider the following measures:
- Gradually increase the intensity of physical activity.
- Maintain a healthy weight.
- Avoid pushing through pain.
- Quit smoking.
- Improve your form during sports and activities.
- Wear orthotics to correct abnormal gait.
- Rest between workouts and stretch before and after physical activity.
How NextPain Approaches Peroneal Tendon Pain
Peroneus brevis tendon pain can significantly impact your daily life. At NextPain Care, we understand the challenges this condition presents, and we’re committed to helping you find relief through our comprehensive three-level treatment approach.
We start with conservative care, emphasizing lifestyle changes, optimal nutrition, and physical therapy to strengthen, stretch, and optimize the tendon for healing. If additional support is needed, we’ll explore other treatments and medications, always prioritizing non-invasive options. Our goal is to ensure a patient-centered approach to your recovery tailored to your specific needs.
Peroneus Tendon Pain Related Conditions We Manage At NextPain Care
Tendon pain can result from various issues concerning the peroneus brevis tendon. The severity can vary from mild discomfort to intense pain, affecting daily activities significantly.
NextPain Care deals with conditions linked to the peroneus brevis tendon pain like:
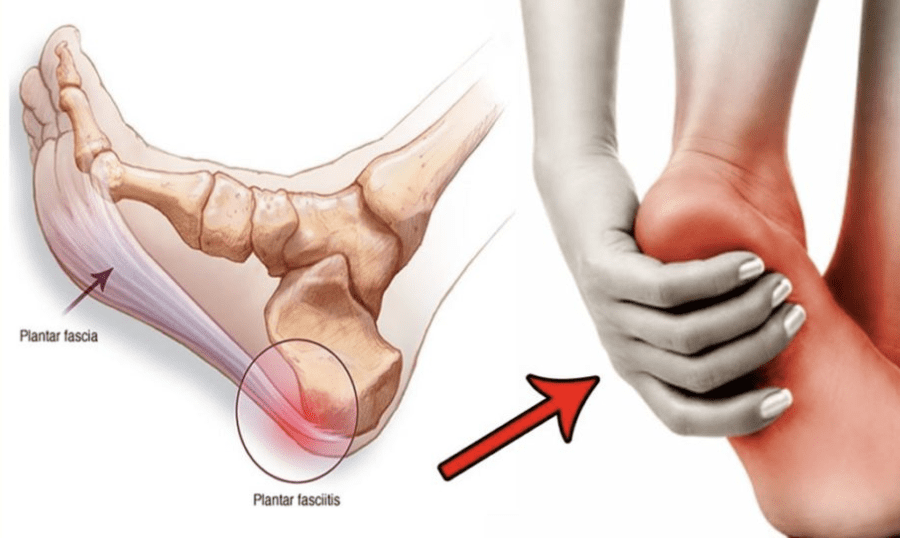
Plantar Fasciitis Pain Treatment
NextPain Care provides pain management for plantar fasciitis, focusing on improving mobility and offering lasting relief from chronic heel pain through personalized...
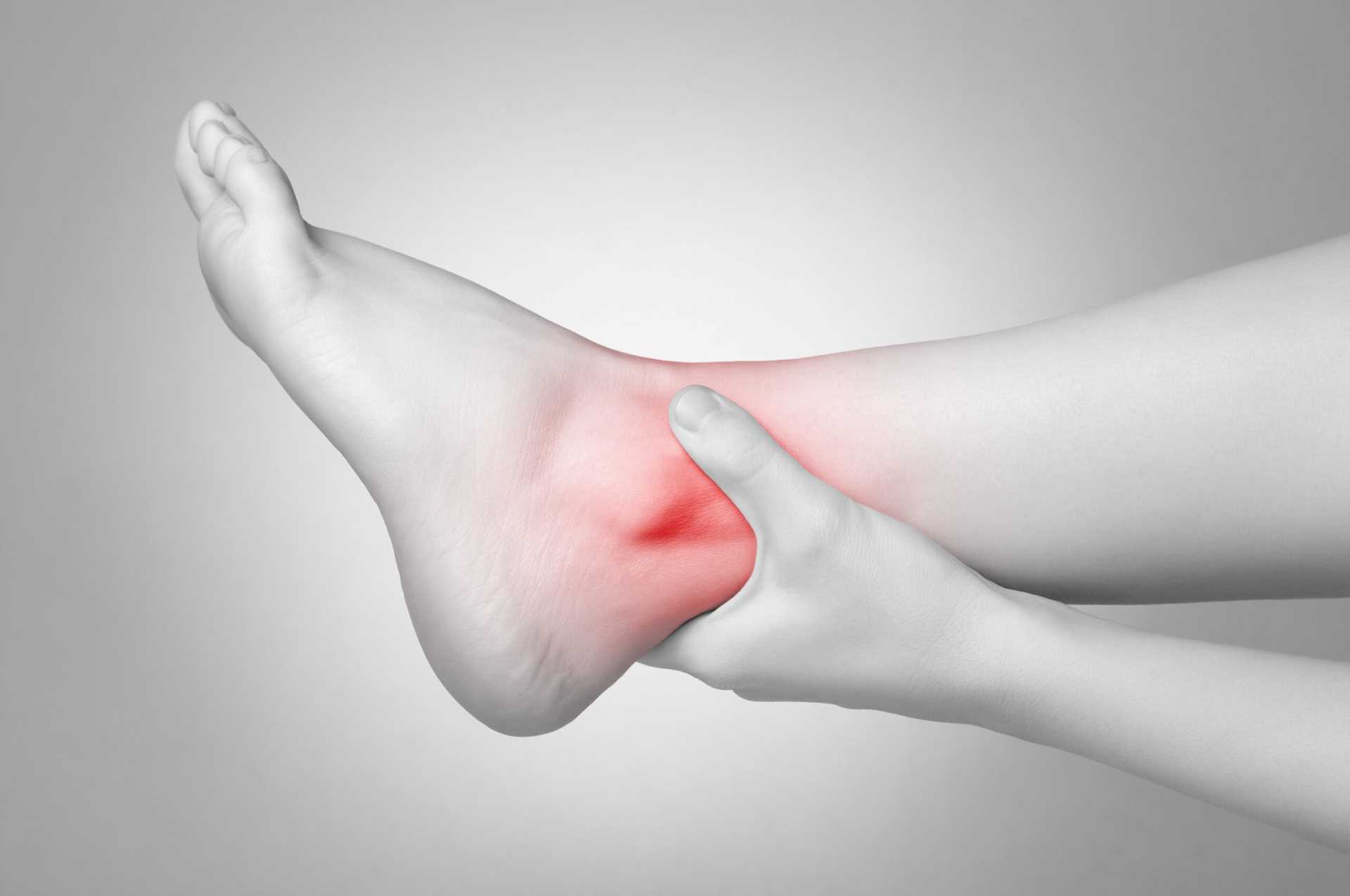
Ankle Sprain Pain Treatment
Ankle sprains often cause significant pain and can sometimes lead to long-term disability. Fortunately, with proper treatment, symptoms can be effectively managed. At NextPain Care, we deliver a comprehensive approach to pain...
Find Lasting Relief with NextPain Care
At NextPain Care, we believe in treating the whole person, not just the symptoms. Our personalized, patient-centered approach ensures that every aspect of your health and well-being is considered.
By tailoring our treatments to your unique needs, we provide care that is not only effective but also compassionate and supportive. This holistic approach helps you achieve the best possible outcomes, allowing you to return to your daily activities with less pain and more confidence.
We are committed to being your partner in health, guiding you towards a more comfortable and active life. Call us today to schedule your personalized consultation, and explore how we can help manage your peroneus brevis tendon pain.
Dealing with peroneal tendon pain? Don’t let it hold you back from living an active life.