If you’ve ever experienced lower back pain accompanied by redness and swelling in your legs and feet, you’re not alone. Affecting over 80% of adults at some point in their lives, back pain is one of the most widespread musculoskeletal disorders, a common reason for missed work days, and a leading cause of disability.
Depending on what’s causing your lower back pain, it may be accompanied by swelling in the lumbar spine, legs, and feet. Edema – or the swelling of tissues – may simply be a consequence of inflammation and fluid build-up, but in some cases, it can be a sign of a more severe underlying condition requiring medical care.
Fortunately, living in fear of experiencing disability, surgical operations, and lifelong pain is no longer the only prospect for people with chronic lower back pain and swelling.
In this guide, we’ll explore how the holistic approach by NextPain Care may help support improved back function, encourage a more active lifestyle, and contribute to enhancing your quality of life.
How Does Swelling Occur In The Lower Back?
Low back pain ranks among the most prevalent and impactful musculoskeletal disorders worldwide. According to a study released in June 2023 by The Lancet Rheumatology, nearly 620 million people globally suffer from low back pain, making it the leading cause of years lived with disability globally. This figure is projected to climb to over 800 million by 2050 due to the expanding and aging global population.
In the United States, a national survey found that three-quarters of individuals dealing with chronic low back pain encounter challenges in various aspects of daily life, such as self-care, mobility, work, and social activities.
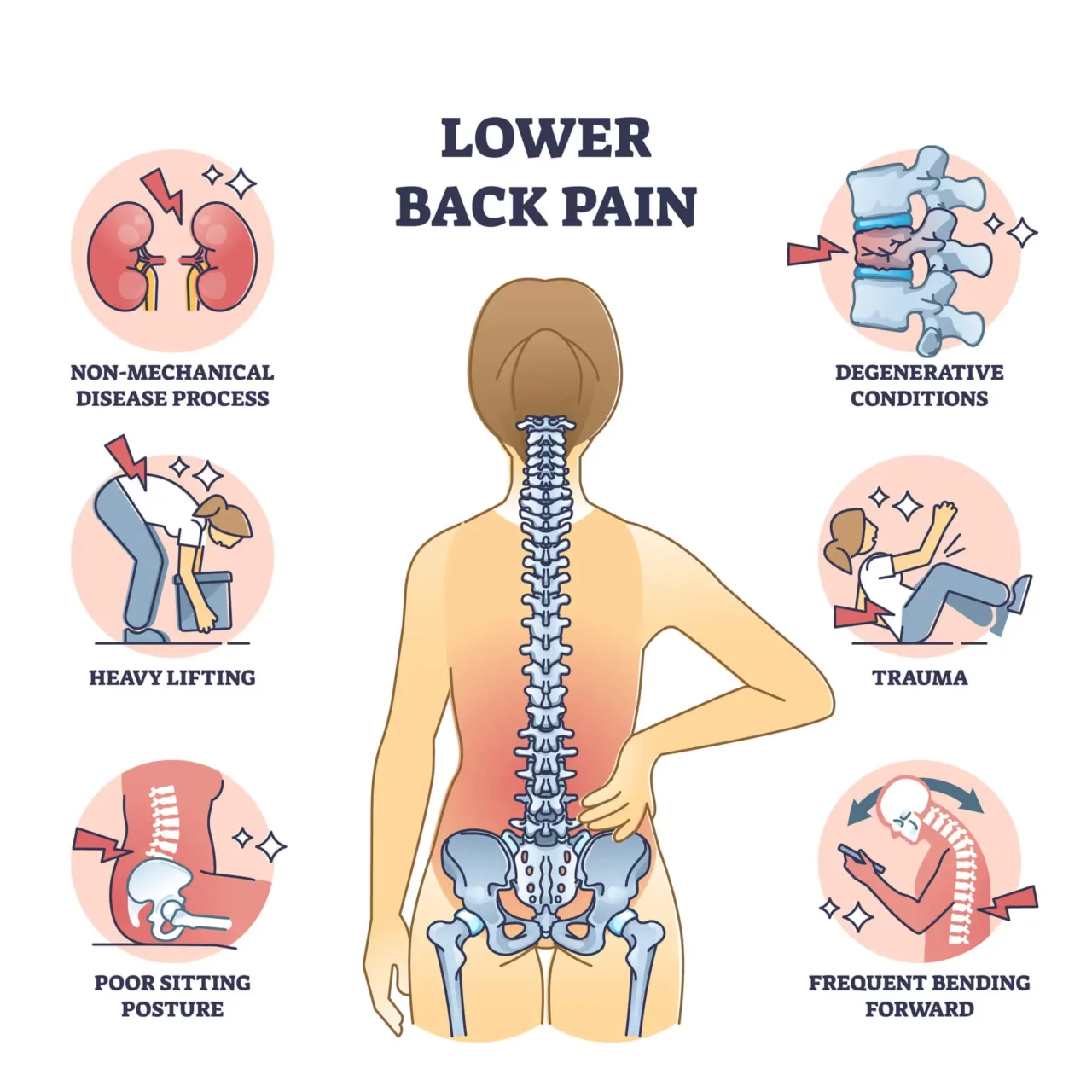
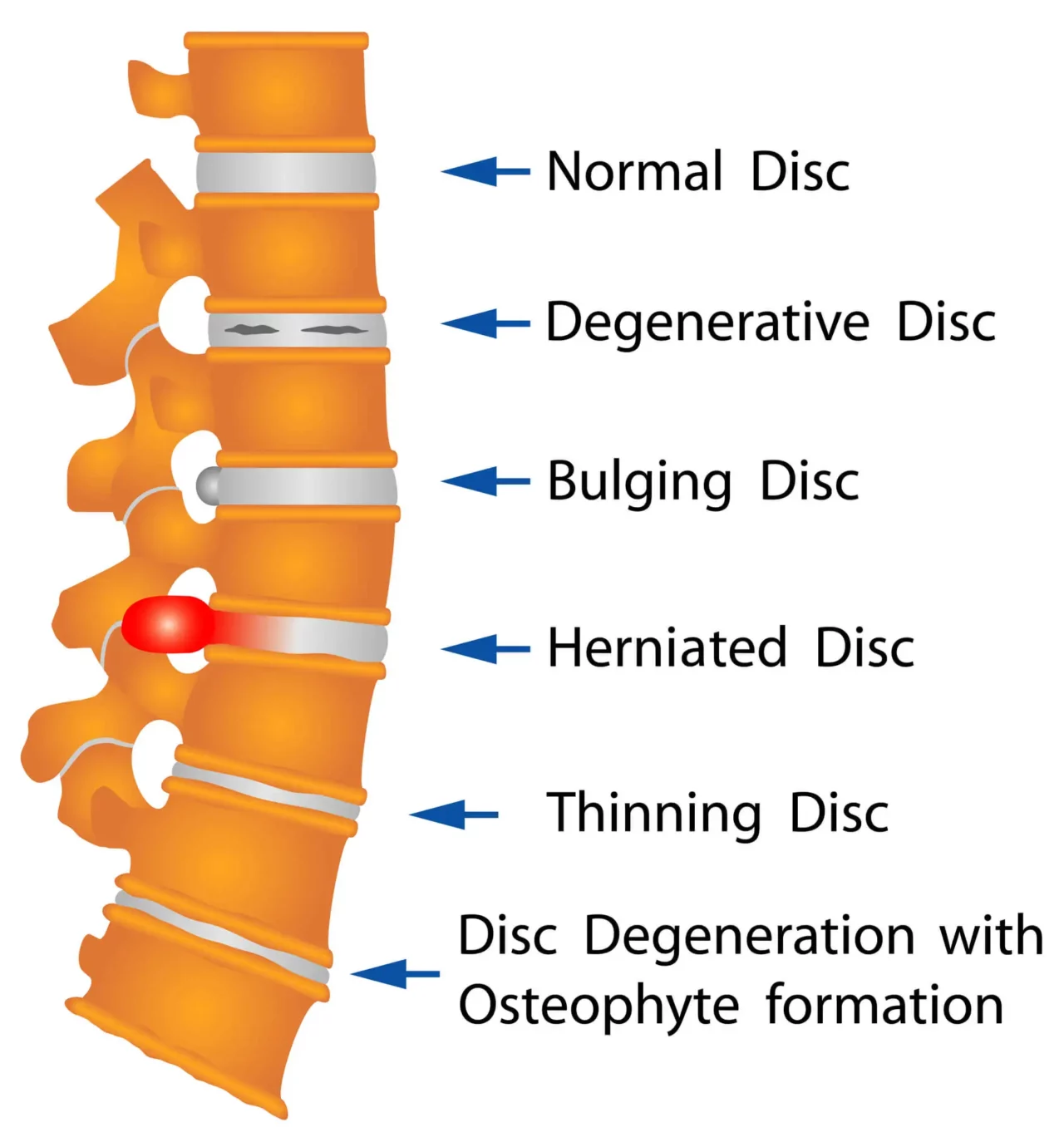
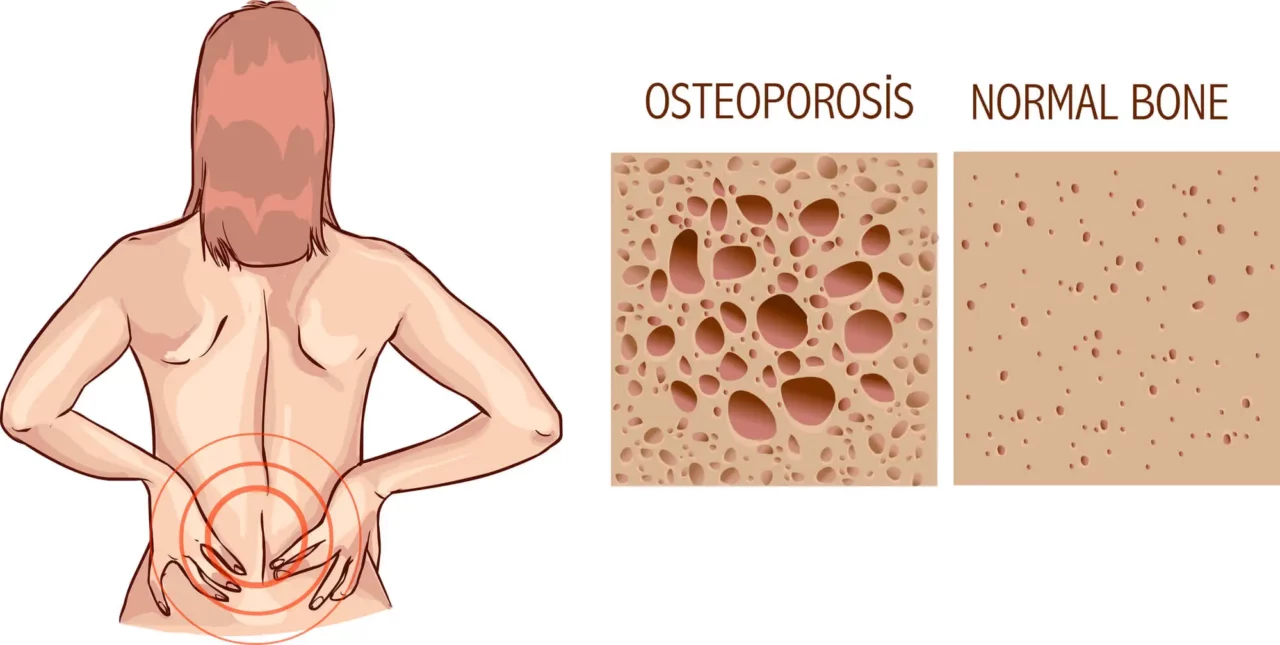
Although low back pain significantly affects quality of life, its causes, nature, and symptoms can vary widely. Typically, it stems from factors such as strain or sprain, poor posture, problems with intervertebral discs, or degenerative conditions like osteoporosis.
Symptoms associated with these conditions may include:
- Sudden or gradual onset of pain in the lumbar spine
- Pain is described as sharp, dull, or achy
- Pain that radiates from the spine to the buttocks and legs
- Audible “popping” noises during the injury
- Increased pain while lying down or during movements such as bending
- Stiffness and reduced mobility, such as difficulty straightening the back, rising from a seated position, or twisting
- Postural changes like leaning forward or appearing crooked
- Painful muscle spasms, often indicative of strains and sprains
At times, lower back pain may coincide with swelling in the lower back.
Lower back swelling, also referred to as edema, arises from fluid accumulation due to the body’s inflammatory response or circulatory issues. While edema is more commonly seen in the legs and feet, it can also affect the lower back. The National Institutes of Health estimates that about 20% of adults experience some form of edema in their lifetimes.
In some instances, lower back swelling is a transient symptom that diminishes with time. For example, trauma or injury to the back prompts an inflammatory reaction aimed at healing damaged tissue, leading to increased fluid circulation and accumulation in the affected area, resulting in swelling. This can typically be managed with rest and ice compresses.
Prolonged immobilization or a sedentary lifestyle can also contribute to edema, as poor circulation causes blood to pool in specific areas such as the back, legs, and feet. Alongside swelling, insufficient circulation may cause redness, numbness, tingling, and, in severe cases, blood clots.
However, noticeable swelling in the lower back may indicate a more serious, potentially life-threatening condition. Conditions such as spinal infections from bacteria in the bloodstream (vertebral osteomyelitis) or inflammatory disorders like sacroiliitis (inflammation of the spine’s base joint) can lead to swelling and require immediate medical attention.
In the following sections, we will explore common pain conditions that, in addition to back pain, may present with symptoms such as lower back swelling, stiffness, redness, and decreased mobility.
Possible Conditions Causing Swelling In The Lower Back
Lower back pain accompanied by redness and swelling can result from strains, sprains, forceful movements, or lifting objects that are too heavy. However, in some cases, these symptoms may stem from chronic pain conditions that can significantly affect your quality of life for months or even years.
Understanding the underlying causes and long-term outlook for low back pain and swelling can assist in preventing complications and finding appropriate treatment. Let’s delve into this topic.
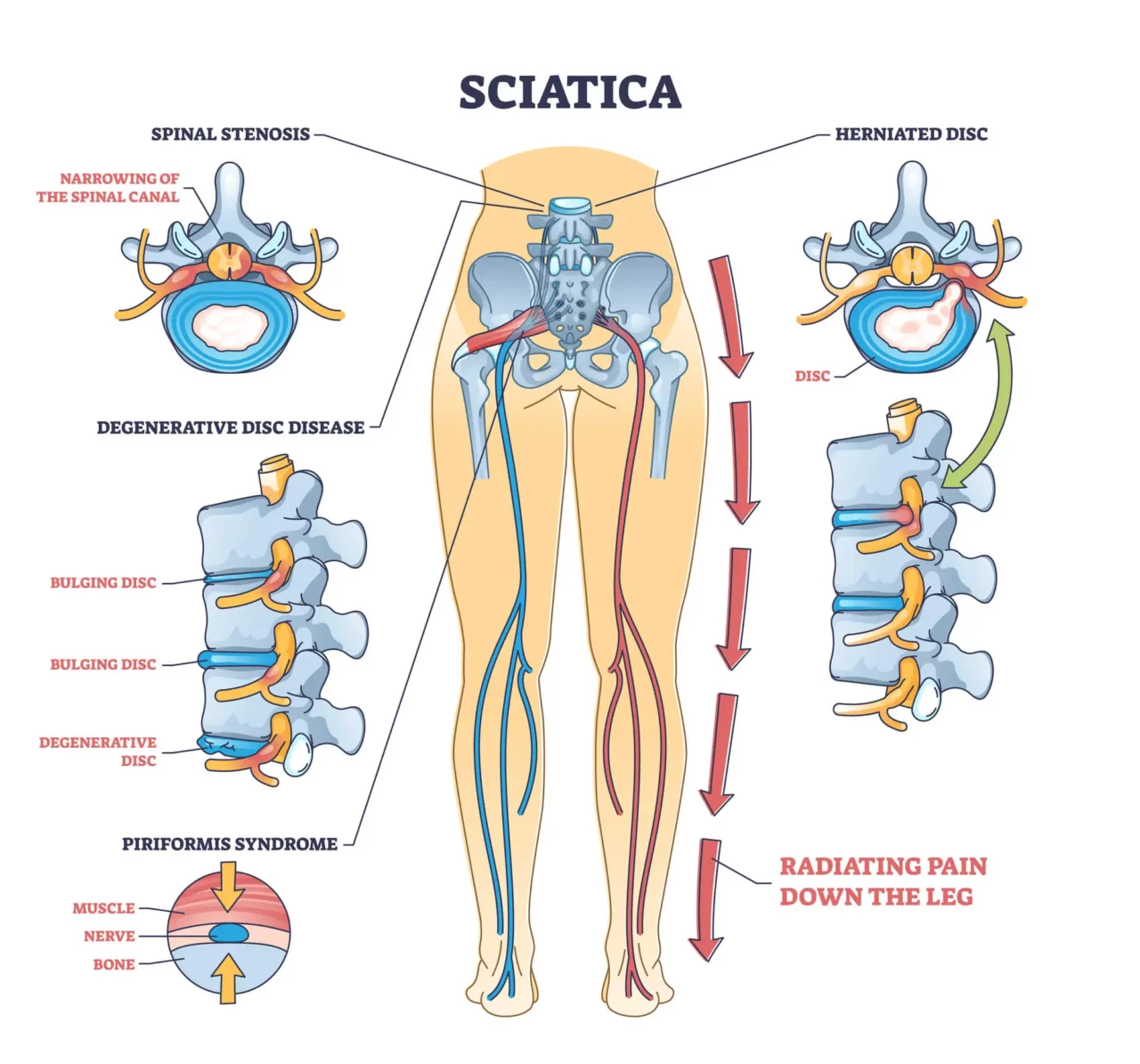
Sciatica
With a diameter of 2cm, the sciatic nerve is the largest nerve in the body. It provides motor and sensory functions to the upper leg, lower leg, and foot. Originating from the lower back, this nerve runs down the back of the leg.
Sciatica refers to any condition that compresses this nerve, impacting its ability to transmit signals to and from the brain. Conditions such as a herniated disc, muscle spasms in the back, spinal misalignments, and tumors pressing on the nerve can all lead to sciatica.
Individuals with sciatica may experience various symptoms, including numbness, tingling sensations, leg weakness, temporary loss of movement, and sharp, stabbing pain that radiates down the hip and leg. Typically affecting one side of the body, sciatica is a chronic condition that affects 10-40% of adults at some point in their lives.
In some cases, sciatica can also cause swelling in the lower back. This occurs when the sciatic nerve is compressed by a herniated disc, spinal stenosis (narrowing of the spinal spaces), or abnormal bony growths (bone spurs).
These structural issues not only press on the sciatic nerve but also irritate surrounding structures, leading to inflammation, fluid build-up, and swelling.
- Tip: Spine anomalies such as bone spurs, tumors, fractures, and herniated discs can also damage a bundle of nerves located in the lower spinal cord. Compression of these nerves can result in a severe condition known as cauda equina syndrome, which leads to loss of bowel and bladder control, loss of sensation in the legs, and difficulty walking. Cauda equina syndrome requires immediate medical attention and often necessitates spinal surgery.
Arthritis
Arthritis refers to conditions that cause inflammation of the joints. Some types of arthritis result from an immune system malfunction, where the body mistakenly attacks healthy tissues, or from metabolic disorders that lead to excess uric acid crystals in the body.
Other types of arthritis, such as osteoarthritis, are known as “wear and tear arthritis” or degenerative arthritis. This form of arthritis develops due to aging, overuse, excessive stress, and mechanical issues. Osteoarthritis commonly affects the knees and hips but can also occur in the lower back, where it is referred to as lumbar or spinal arthritis.
In spinal arthritis, the cartilage, which normally acts as a shock-absorbing cushion between the bones, wears down. This exposure of bones to friction and shock leads to pain, stiffness, mechanical problems, loss of mobility, and, over time, disability.
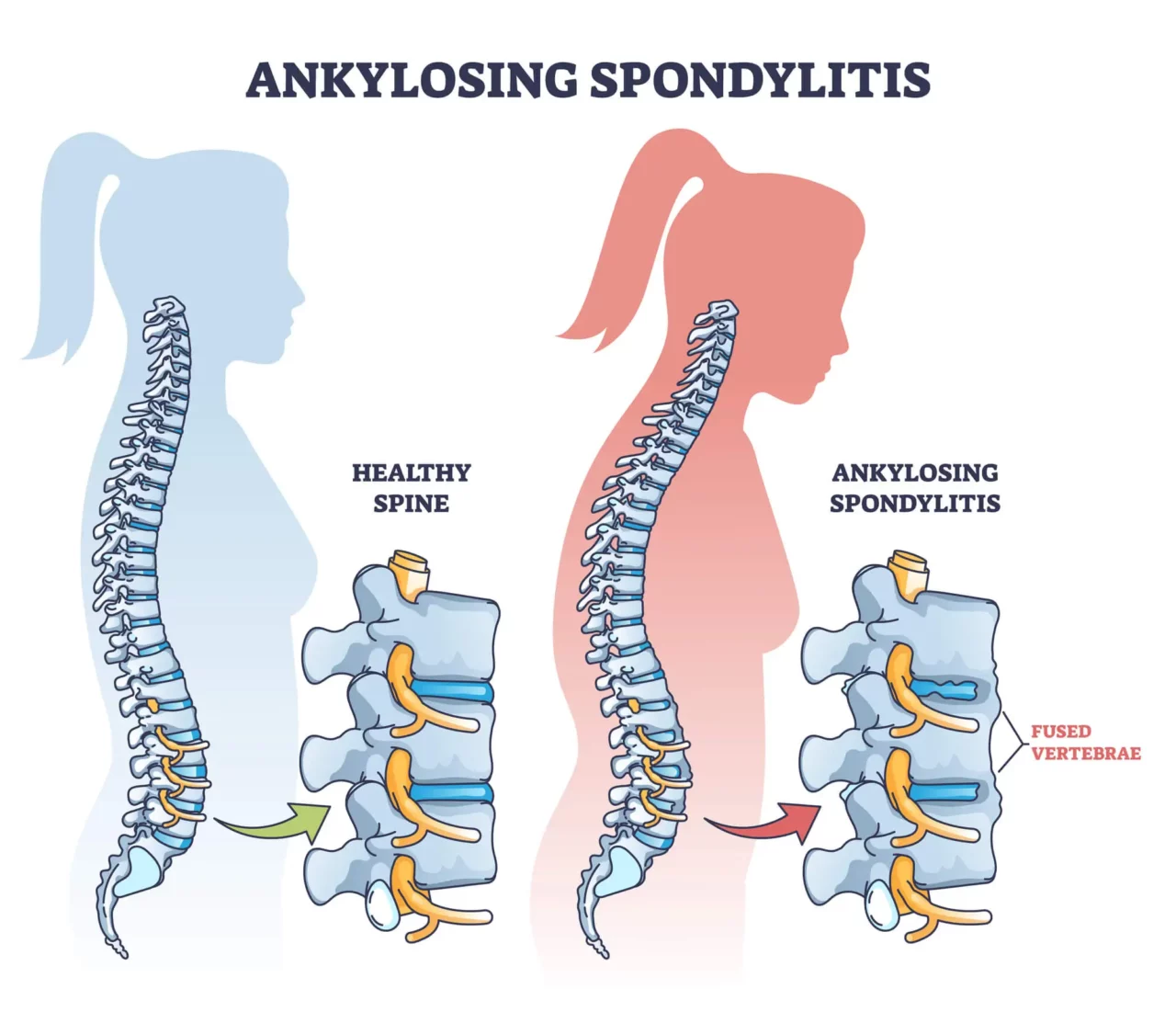
Ankylosing spondylitis is another form of arthritis that typically affects the back and neck. Caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors, it leads to chronic inflammation of the spine’s joints and surrounding structures like ligaments and tendons. If untreated, this condition can cause the bones of the spine to fuse together, resulting in a significant loss of movement and flexibility.
Risk Contributors
Low back swelling is often linked to conditions causing inflammation and pain in the lumbar spine, such as sprains, strains, disc injuries, and arthritis. These conditions share common risk factors and causes.
Below, we explore the environmental, health, and lifestyle factors that may contribute to low back swelling.
- Age: Disc degeneration is a natural part of aging, making disc tears and herniations more common in individuals aged 30 to 50. Aging can also accelerate bone mass loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis in older adults.
- Obesity or being overweight: A high body mass index (BMI) accounts for over 12% of the disability years experienced by individuals with chronic back pain. Excess weight can accelerate disc degeneration and put excessive pressure on the spine.
- Overall health status: A sedentary lifestyle, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking are lifestyle factors associated with a higher risk of low back pain, inflammation, and swelling. Poor core muscle conditioning also increases the likelihood of injuries such as strains.
- Occupation and lifestyle: Jobs and hobbies involving forceful or repetitive twisting motions, heavy lifting, bending, and jumping can raise the risk of back injuries and speed up intervertebral disc degeneration.
- Spine alignment: Mechanical issues like poor posture and structural problems such as scoliosis or spinal stenosis can cause back pain. These conditions alter spine mechanics, causing friction damage to ligaments and bones, leading to pain, swelling, and compression of nearby spinal nerves.
- Comorbidities: A family history of osteoarthritis and other inflammatory conditions may increase the risk of chronic back pain and swelling. Tumors and abnormalities affecting the spine and spinal cord can also cause pain, numbness, tingling sensations, and swelling.
Low back pain is also associated with mental health disorders like depression. Given the diverse causes, habits, and conditions leading to back pain and swelling, obtaining an accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment.
When To Seek Medical Help For Lower Back Swelling
Lower back swelling and pain can indicate a more serious or long-term health issue. It’s important to know when to see a doctor for these symptoms.
- Tip: If you experience sudden or severe swelling accompanied by symptoms like severe headaches, loss of bladder and bowel control, difficulties with walking and balance, or trouble speaking, seeking immediate medical care is crucial.
Here are some symptoms that should prompt you to seek medical attention:
- Swelling without prior conditions or injuries: If you experience back swelling without a clear cause or previous injury, it could be a sign of ankylosing spondylitis, a chronic inflammatory disease that primarily affects the spine, causing stiffness, pain, and swelling in the lower back.
- Pain lasting more than one month: If pain and swelling persist for over a month, it may indicate a condition more serious than temporary sprains or strains. Visiting a healthcare provider can help identify the root cause, which might be a long-term condition like arthritis.
- Tingling, numbness, and weakness in the back and legs: If lower back swelling and pain come with loss of sensation and muscle strength radiating through the legs, it may be due to nerve issues. Conditions such as spinal stenosis, disc herniation, cauda equina syndrome, and sciatica can cause these symptoms.
- Redness and warmth in the legs: Swollen or red legs, accompanied by a sensation of warmth, may indicate blood circulation issues. This could be due to a sedentary lifestyle or conditions like varicose veins and chronic vein insufficiency.
- Fever and chills: Fever and chills along with swelling and pain might suggest your body is fighting a spine or intervertebral disc infection.
- Nausea and vomiting: Certain infections, like cellulitis, can develop into more serious conditions such as osteomyelitis (bone infection) and meningitis (infection of the membrane around the brain and spinal cord). These infections cause radiating pain, swelling, fatigue, nausea, and vomiting and require immediate medical care.
- Diarrhea: Severe conditions, including kidney infections or failure, can cause back pain and diarrhea.
Lower back swelling can also be a symptom of pregnancy complications or issues with the female reproductive organs, as well as potentially serious conditions like an abdominal aortic aneurysm. Obtaining an accurate diagnosis is essential to determine the cause of your back pain or swelling and to find appropriate treatment.
How To Diagnose Swelling In The Lower Back
While there isn’t a singular diagnostic test for back pain, healthcare providers employ various methods to pinpoint the underlying cause of any discomfort or swelling you may have. Initially, your doctor will review your medical history and symptoms, followed by conducting a thorough medical examination.
Healthcare providers can also prescribe more in-depth tests, such as the following:
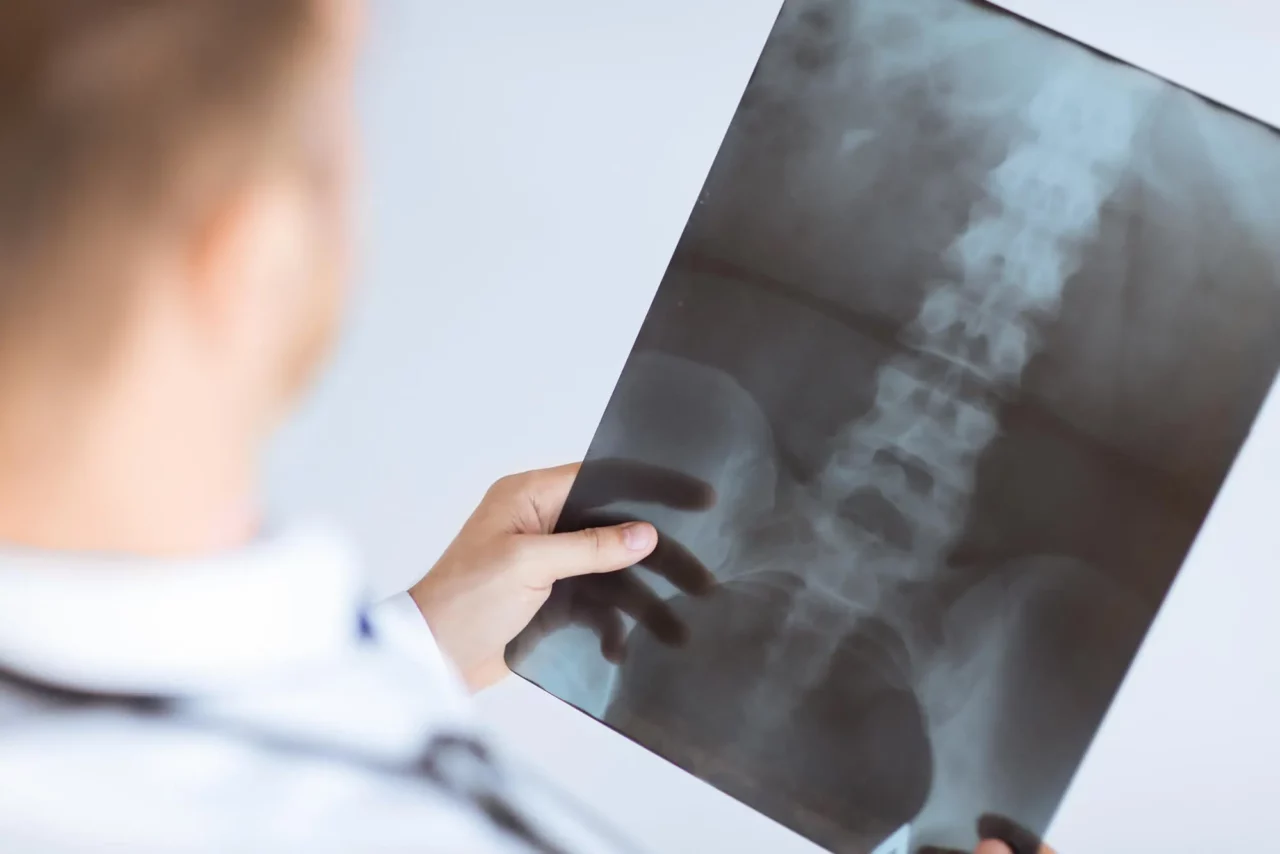
- X-rays: X-rays use radiation that passes through the body to create images of bones and other structures, helping to identify anomalies, including tumors.
- MRIs: Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) uses radio waves and magnets to create detailed pictures of the inner lower back, including ligaments, tendons, muscles, and bones.
- CT scans: CT scans utilize X-ray technology to generate detailed 3D images of the spine and surrounding structures, aiding in the identification of specific causes of low back pain, such as herniated discs or spinal stenosis.
- Electromyography: This test measures the electrical activity in muscles and assesses the nerves’ ability to transmit sensory and motor signals, helping to determine if back pain is due to a nerve or muscle issue.
Other tests that may be used to determine the root cause of pain and swelling in the lower back include blood tests, bone density tests, and neurological exams.
Conventional Treatment Options
If you have chronic or acute low back pain with swelling and stiffness, you may benefit from home remedies and conventional treatments to manage your symptoms. These therapies can be helpful in temporarily relieving discomfort and improving mobility.
Here are some treatment options to consider:
- Rest: Taking time to rest can relieve pressure on your lower back, particularly if your pain is due to compression injuries like disc herniation or degeneration. This can help restore sensation and mobility by reducing nerve pressure.
- Heat/ice therapy: Alternating between hot and cold compresses can effectively reduce inflammation, ease muscle tension, and improve mobility. Use heat for older injuries to promote blood flow and healing, and use ice to reduce swelling and fluid buildup in new injuries.
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Non-prescription pain relievers and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory medications (NSAIDs) can provide relief during a flare-up.
- Stretching: Gentle stretching exercises can alleviate muscle tension and reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve and spinal cord nerves. This helps to reduce inflammation, enhance blood circulation, and relieve pain. For those with chronic back pain, regular stretching can also decrease disability.
- Physical therapy: Engaging in physical therapy can strengthen the muscles of the back, legs, and core, which are crucial for supporting the spine, distributing loads, and preventing injuries.
- Massage therapy: Massages can release the body’s natural pain-relieving hormones (endorphins), reduce muscle tension, and alleviate pressure on spinal structures.
- Acupuncture: This involves inserting fine needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system, prompting the release of endorphins and other pain-relieving chemicals, which can help reduce lower back pain and inflammation.
- Chiropractic adjustments: Chiropractic care involves spinal manipulation to restore proper movement and function. It can reduce pain, swelling, and disability caused by pinched nerves, mechanical issues, and poor posture.
- Epidural injections: Steroid injections into the epidural space of the spine can decrease inflammation and swelling in the spinal nerves, alleviating pain and improving mobility, especially in the lumbar region.
NextPain Care provides evidence-based, minimally invasive treatments within a comprehensive approach, ensuring you receive the fundamental and appropriate care tailored to your needs. We support our patients at every level, offering advanced options when necessary to effectively manage your pain with guidance from our dedicated healthcare professionals.
How NextPain Care Treats Conditions Causing Lower Back Swelling
When managing conditions that cause lower back swelling and pain, NextPain Care takes a comprehensive approach that considers various health and lifestyle factors, including nutrition and sleep habits.
Our 3-level system begins with conservative care and advances to more tailored treatments as needed. Depending on your condition, a variety of treatment options are available, including therapies such as intrathecal pain pumps, nerve blocks, or spinal cord stimulation. These are just some of the many options we offer to help manage conditions that cause back pain, all tailored to your individual needs.
We follow evidence-based practices endorsed by leading authorities like the AMA and WHO, aiming to address the root of your discomfort and support long-term health.
Conditions We Help Manage To Relieve Lower Back Discomfort
Osteoporosis Pain Treatment
Although osteoporosis doesn't directly cause chronic pain, it can lead to conditions such as bone fractures, joint pain, and nerve damage that result in chronic pain. This pain can be debilitating. At NextPain Care, we manage osteoporosis with our three-level...

Sciatica Pain Treatment
Sciatica can cause intense pain and discomfort, making daily activities challenging. At NextPain Care, we provide a comprehensive approach to managing sciatic pain and associated symptoms, offering treatments designed to improve your comfort and mobility over...
Neck and Back Pain Treatment
Nothing can be as debilitating as chronic neck and back pain. Fortunately, NextPain Care provides a comprehensive approach that aims to manage the underlying cause of your pain....
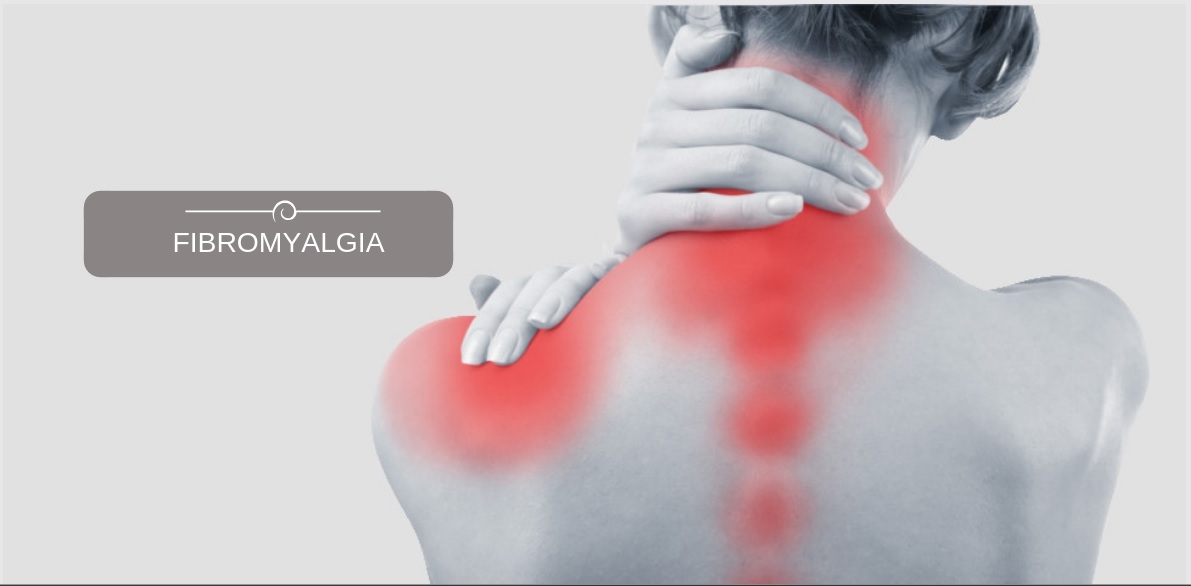
Fibromyalgia Treatment
Fibromyalgia is a chronic condition characterized by widespread pain, fatigue, and other challenging symptoms such as tender points and sleep disturbances. At NextPain Care, we use evidence-based approaches to help manage the painful symptoms of...
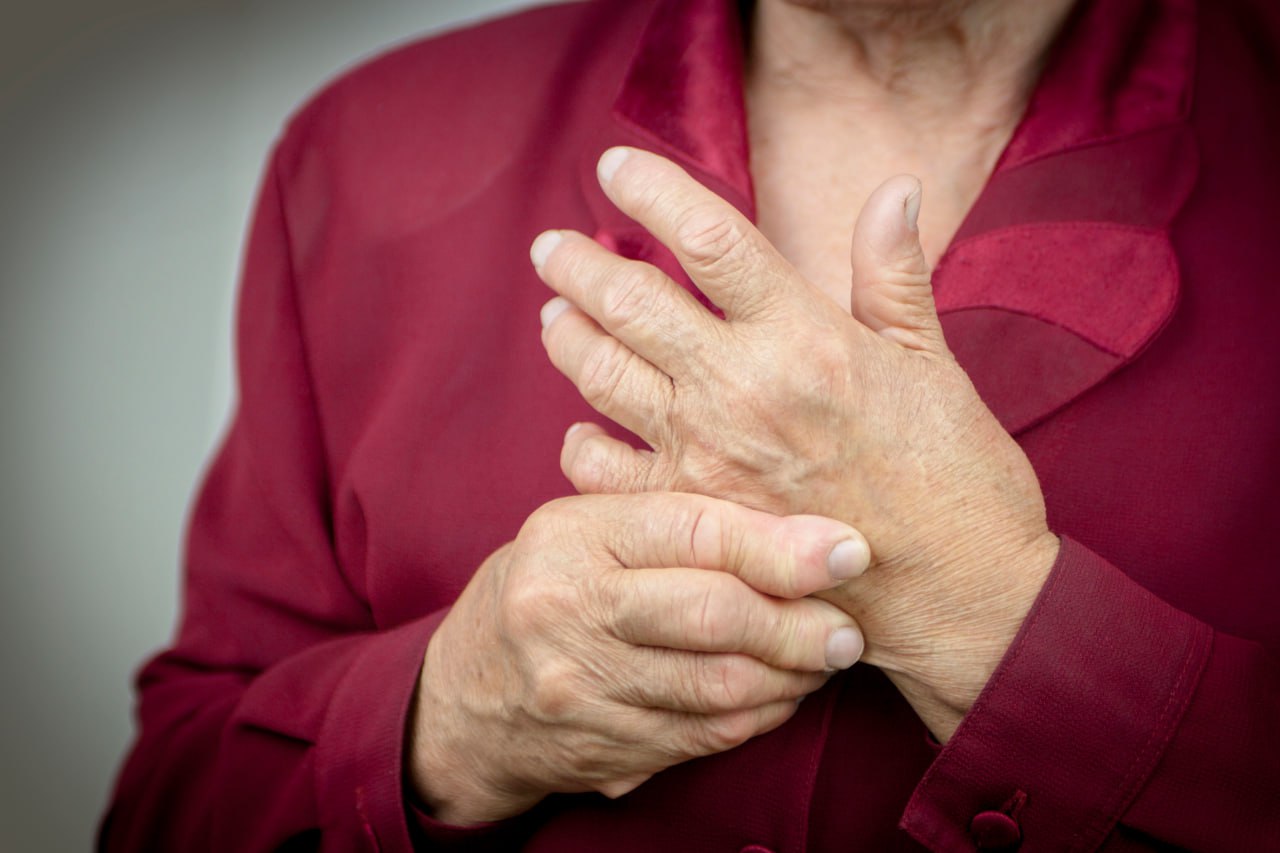
Rheumatoid Arthritis Pain Treatment
Rheumatoid arthritis can be a debilitating and painful condition that causes swelling, joint damage, and immobility. NextPain Care offers a comprehensive approach to treating the pain associated with rheumatoid arthritis and the condition itself. We aim to...
Find Expert Care For Lower Back Swelling Now
Lower back swelling and pain can significantly affect both your professional and personal life, leading to discomfort and reduced mobility. Finding an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment can often be challenging.
At NextPain Care, our dedicated team of healthcare professionals uses comprehensive diagnostic tests to identify the specific factors contributing to your discomfort. We focus on addressing the root causes of your lower back pain and swelling, not just the symptoms.
Our personalized treatment plans range from conservative options and minimally invasive therapies to advanced medical interventions, all aimed at supporting spine health and improving your overall well-being. By taking a holistic approach, we strive to provide relief that helps you lead a more active and fulfilling life.
Don't let lower back swelling or redness slow you down.