A broken wrist is a relatively common injury that can happen to anyone. This type of fracture typically occurs from direct impact to the wrist, such as a sports injury or a fall onto an outstretched hand. A broken wrist can significantly impact your daily activities and hinder your ability to use your hand correctly.
Even after the initial treatment and healing process, proper care and rehabilitation are crucial for maintaining long-term wrist health.
What Is A Distal Radius Fracture?
A distal radius fracture is a wrist injury that specifically affects the radius bone, one of the two long bones in the forearm that run from the elbow to the wrist. The distal end of the radius is located at the wrist joint and connects the hand to the forearm. The wrist joint contains eight small bones that allow the hand and arm to have a wide range of motion. A distal radius fracture can vary in severity, from a mild crack to a complete break through the bone.
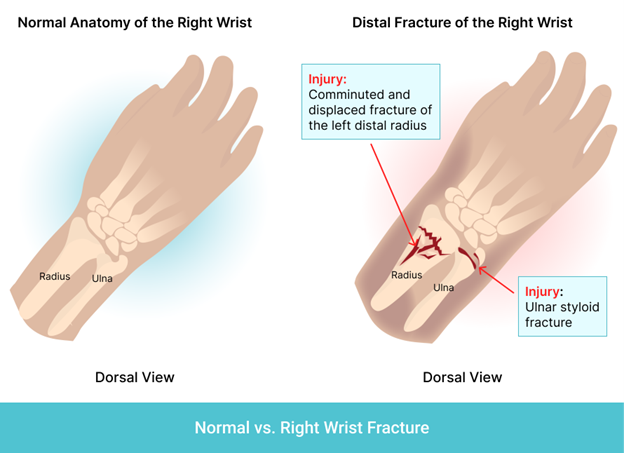
Comparing A Normal Wrist And A Fractured Wrist
In a normal wrist, the radius and ulna bones work together to support the hand and allow for movement. The joint between these two bones is covered in cartilage, which helps reduce friction and allows for smooth movement. Ligaments, tendons, and muscles also play a crucial role in supporting the wrist joint.
In a fractured wrist, one or both of these bones may be broken, disrupting the proper alignment and stability of the joint. This can lead to pain, swelling, and difficulty moving the hand and wrist.
Different Kinds of Wrist Bone Fractures
The wrist consists of several small bones where different types of fractures can occur, including:
- Scaphoid fracture: A fracture of the scaphoid bone, located on the side of the wrist leading up to the thumb. This type of fracture can affect the stability and function of the wrist joint due to its location and role in supporting the thumb.
- Distal radius fracture: As noted above, this fracture occurs at the end of the radius bone near the wrist joint and is one of the most common types of wrist fractures.
- Chauffeur’s (radial styloid) fracture: This fracture affects the radial styloid, a small bony bump on the thumb side of the wrist.
- Barton’s fracture: This type of fracture occurs when the wrist joint is dislocated, causing the bones to break. It can have serious implications and may require surgery for proper treatment due to the complexity of the injury.
- Ulnar styloid fracture: This fracture affects the ulnar styloid, a small bony bump on the pinky side of the wrist.
Pain and Other Symptoms of Fractures in the Wrist
Wrist fractures often result in significant pain and discomfort, especially during movement. In addition to pain, other common symptoms of a broken wrist include:
- Bruising: Discoloration of the skin caused by damaged blood vessels leaking blood into the surrounding tissues. Bruising is common in wrist fractures due to the trauma that caused the injury.
- Bone swelling: Known as periosteal edema, this is a buildup of fluid in the tissues surrounding the fracture site. It can cause visible swelling or a bump near the broken bone and may feel firm to the touch. This swelling results from inflammation in response to the fracture.
- Inability to move the wrist: A fractured wrist can make it difficult or impossible to move the hand and fingers normally due to the pain, swelling, and instability caused by the fracture. In severe cases, the wrist may become completely immobilized.
Weakness In Hands
Experiencing persistent weakness in your hands can greatly affect your quality of life. It can make everyday tasks difficult, especially if your job requires manual dexterity. Weak hands can make it challenging to pick up objects or grip tools effectively,...
Understanding Pain and Tenderness When Touch
The signs and symptoms of tenderness and pain can vary depending on the underlying cause. Typically, individuals experiencing this sensation feel significant discomfort when their skin is touched or pressed. This pain may be accompanied by localized...
Read More About Understanding Pain and Tenderness When Touch
Exploring The Feeling Of Numbness
Experiencing numbness in your body can be unsettling and uncomfortable. Known as paresthesia, this sensation manifests as tingling or prickling that can occur throughout the body, often described as "pins and needles" or a lack of...
Common Causes of Wrist Fractures
Understanding the causes and risk factors of wrist fractures can help in preventing future injuries.
The most common causes of a wrist fracture include:
Age
As we age, our bones become more brittle and prone to fractures. This is due to the decrease in bone tissue production and calcium levels, making bones weaker and more susceptible to breaks. Additionally, older individuals are at a higher risk of falling, further increasing the likelihood of wrist fractures.
Gender
Women are more likely to experience wrist fractures, especially after menopause. Hormonal changes during this period can reduce bone density, weakening bones. These changes can also affect coordination and balance, increasing the risk of falls.
Falls and Accidents
Falls, particularly onto an outstretched hand, are the leading cause of wrist fractures. Car accidents and other high-impact incidents can also result in wrist fractures.
Injuries or Trauma
Sports-related impacts or direct trauma to the wrist can cause fractures. For instance, a direct blow to the wrist during activities like softball or football can lead to a fracture. Repetitive stress injuries, such as those experienced by gymnasts from repeatedly landing on their hands, can also contribute to wrist fractures.
Medical Conditions
Certain medical conditions can weaken bones and increase the risk of fractures. Managing these conditions is crucial to preventing future injuries. The following conditions are linked to an increased risk of wrist fractures:
- Osteoporosis: Characterized by brittle and weak bones, osteoporosis makes bones more prone to fractures. It commonly affects older individuals, postmenopausal women, and those with a family history of the disease.
- Osteogenesis Imperfecta: Also known as brittle bone disease, this genetic disorder causes bones to be more fragile and prone to fractures.
- Cancer: Cancer can weaken bones, making them more susceptible to fractures. Certain cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy, may also reduce bone density, increasing the risk of fractures.
Potential Risks Associated with an Untreated Broken Wrist
Seeking medical treatment for a broken wrist as soon as possible is crucial. Leaving a fractured wrist untreated can lead to several risks and complications, including:
- Malunion: This occurs when a bone heals in an incorrect position, resulting in permanent deformity and reduced hand and wrist function.
- Nonunion: Nonunion happens when a bone fails to heal after an extended period, leading to chronic pain and decreased mobility.
- Nerve Damage: A broken wrist can cause nerve damage, leading to symptoms such as tingling, numbness, and weakness in the hand and fingers.
- Arthritis: Damage to the cartilage or joint surfaces of the wrist from a fracture can lead to arthritis, causing persistent pain and stiffness in the joint.
- Compartment Syndrome: In rare cases, a broken wrist can result in compartment syndrome, a serious condition caused by increased pressure within a muscle compartment. This can cut off blood flow and damage nerves and muscles. If left untreated, compartment syndrome can be life-threatening.
Diagnosing a Wrist Fracture
If you are experiencing any symptoms of a wrist fracture, it is vital to seek medical attention immediately. A doctor will perform a physical exam and may order diagnostic tests to confirm the fracture. These tests may include:
- X-ray: The most common diagnostic test for bone fractures, X-rays create images of bones using low levels of radiation.
- CT Scan: A CT scan provides more detailed images than a regular X-ray and helps identify more complex fractures and determine their severity.
- MRI: An MRI produces detailed images of bones and soft tissues using powerful magnets and radio waves. This test is often used to examine complex fractures or detect any nerve or ligament damage.
- Bone Scan: A bone scan involves injecting a small amount of radioactive substance into the bloodstream, allowing doctors to detect areas of increased bone activity, which can indicate a fracture.
- Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry (DXA): This test measures bone density and can help diagnose osteoporosis.
Conventional Treatment Options
For treating wrist fractures, many healthcare professionals recommend conventional methods. Some of the common treatment options include:
Medications
Over-the-counter (OTC) pain relievers like acetaminophen or ibuprofen can help alleviate pain and swelling. In more severe cases, a doctor may prescribe stronger pain medication. These medications can help manage symptoms, but do not aid directly in the healing of the fracture.
Immobilization
Immobilizing the wrist helps alleviate pain and prevent further injury. This is typically achieved through splinting or casting, which keeps the bones in proper alignment during the healing process.
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy is crucial for regaining mobility, flexibility, and strength in the wrist after a fracture has healed. A physical therapist may recommend exercises to improve grip strength and prevent future injuries.
Surgery
Surgery is usually reserved for more severe fractures or cases where the bones are not properly aligned. It is an acceptable option determined by a healthcare professional without referring to it as harsh or inherently bad. Surgery can carry risks, such as complications or infection, as it involves cutting the skin and using screws, pins, or plates to hold the bones in place.
There are two main types of surgery used to treat wrist fractures:
- Closed Reduction: This procedure involves manipulating the bones back into place without making any incisions. It is typically performed under local or general anesthesia and can be done on an outpatient basis. While less invasive, there is still a risk of nerve or further bone damage if the bones are not aligned correctly.
- Open Reduction: This surgery involves making an incision to realign the bones and then using plates, screws, or pins to hold them in place. It is a more invasive approach that may require a hospital stay and carries a higher risk of infection or nerve damage. Additionally, the recovery time for this surgery is longer compared to closed reduction.
The NextPain Care Approach for a Broken Wrist
At Next Pain Care, we understand how challenging a broken wrist (distal radius fracture) can be and are committed to providing effective, evidence-based treatments to help you heal and regain your quality of life. We start with minimally invasive treatments designed to promote healing and reduce pain with minimal disruption to your daily activities. If these initial treatments do not provide enough relief, we offer more advanced options to target your pain and facilitate recovery more directly.
Our multidisciplinary team creates personalized treatment plans tailored to your specific needs, ensuring you feel comfortable and supported throughout your journey. At Next Pain Care, the treatment approach we offer for a broken wrist includes:
Mindfulness and Meditation for Chronic Pain
Mindfulness and meditation are techniques used to manage chronic pain by promoting relaxation and mental focus. NextPain Care incorporates these practices into its holistic approach to pain management, helping patients reduce pain perception and improve their...
Epidural Steroid Injections
Epidural steroid injections deliver anti-inflammatory medication directly to the site of pain. At NextPain Care, these injections are used to reduce inflammation and pain in various acute and chronic conditions. This minimally invasive treatment involves the...
Support Your Wrist’s Recovery
Our mission at NextPain Care is to help patients rediscover the joy of living by offering comprehensive and personalized treatment plans for pain relief. By addressing the underlying causes of wrist pain, we provide safe and effective options alongside traditional treatments.
Our experienced team is dedicated to delivering the highest quality care. Contact us today to learn more about our approach and how we can support your recovery from a wrist fracture.
Our Providers
We are extremely proud of our providers’ depth of ability and knowledge as they work tirelessly to enhance our patients’ health outcomes every day.

Take proactive steps to alleviate the pain associated with wrist bone fractures.

