What Is Trigeminal Neuralgia?
Also known as tic douloureux (painful tic), trigeminal neuralgia (TN) is a chronic, lifelong condition that causes agonizing pain. The painful episodes usually focalize on one side of the face, develop in a matter of seconds, and can disrupt your daily life.
The pain stems from a problem with the trigeminal nerve, which is a set of cranial nerves starting from the top of the ear and splitting off across the side of the face. Although you have two trigeminal nerves – one for each side of the face – TN usually affects only one of these nerves.
In people with TN, the dysfunction of the trigeminal nerve often occurs due to a blood vessel pressing on and damaging the nerve. However, this condition may also have other causes, such as tumors, surgical injuries, facial trauma, or multiple sclerosis.
The pain deriving from this disease is often described as an electric shock-like, stabbing sensation, so intense that it can prevent you from drinking, eating, smiling, or speaking.
The Prevalence, Incidence, and Impact of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia is considered a rare disorder, affecting around 5.5 people per 100,000. Only around 15,000 new cases of TN are registered annually in the US, and women – especially those aged 50 and over – are twice as likely as men to experience it.
Despite its rarity, this condition can be extremely severe. The painful episodes it causes are unpredictable and agonizing, leading to significant mental and physical distress. Currently, there is no definitive cure for TN. Surgical interventions may help suppress symptoms temporarily, while pharmaceuticals can help manage pain.
Because of the lack of a cure and the intense pain, trigeminal neuralgia can significantly impact mental health. In a 2018 study, TN accounted for 26% of all attempted suicides in people with chronic headache disorders.
Fortunately, today’s patients have hope for an effective treatment option that does not involve pharmaceuticals or surgery.
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Trigeminal Nerve
Trigeminal neuralgia results from disruptions in the function of the trigeminal nerve. This can occur when a blood vessel comes into contact with and compresses the nerve, although other conditions can also cause trigeminal nerve damage.
To understand how TN relates to trigeminal nerve damage, let’s explore the function and anatomy of this nerve.
The Function Of The Trigeminal Nerve
The trigeminal nerve is one of the 12 pairs of cranial nerves stemming from the brain and spreading throughout the body. These nerves are responsible for transmitting signals to the brain related to sensations, pain, touch, vibration, muscle movements, and bodily functions such as heartbeat and digestion. These signals are processed by the brain, enabling you to move your muscles and experience sensations in response to stimuli.
The trigeminal nerve, in particular, branches out into the face and is responsible for transmitting pain, touch, and temperature sensations from your face to the brain.
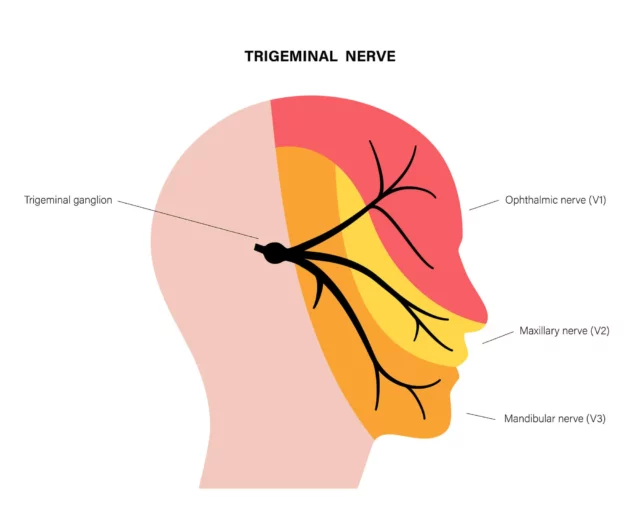
Trigeminal Nerve Branches
There are two trigeminal nerves, one located on each side of the face. Each nerve starts near the top of the ear and then splits into three branches:
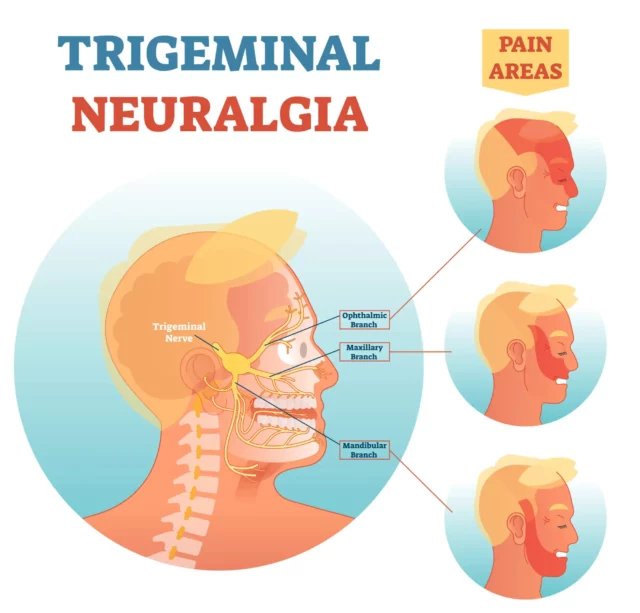
- The Ophthalmic Branch: This is the upper branch of the trigeminal nerve. It spreads across the scalp and forehead, transmitting signals to the brain relating to the upper portion of your head.
- The Maxillary Branch: This branch connects the middle portion of your face to the brain, including the cheek, upper jaw, nostrils, and upper lip.
- The Mandibular Branch: The lower branch supplies nerve endings in the lower jaw area, bottom lip, teeth, and gums.
Role In Facial Sensation
The trigeminal nerve transmits sensations from various parts of the face to the brain. This connection can be disrupted due to nerve damage, which may occur if the trigeminal nerve is compressed, irritated, or inflamed.
When this nerve is damaged, it can misfire, causing sudden electric shock-like sensations. Pain may also be triggered by normally painless stimuli, such as brushing your hair, touching your face, or putting on makeup.
Although it may feel like the pain affects the entire side of your face, it typically centers around the area where one of the nerve branches is irritated or damaged. The intensity of trigeminal neuralgia pain is often reported to be more severe than a heart attack or childbirth.
Types of Trigeminal Neuralgia
Trigeminal neuralgia consistently causes excruciating pain, but the intensity, pattern, frequency, and location of flare-ups can vary among individuals.
In most cases, painful sensations occur in intermittent bouts, characterized by stabbing sensations. Some people may also experience constant aching or burning pain.
Depending on your symptoms, your condition may be classified as classic trigeminal neuralgia or atypical trigeminal neuralgia. Let’s explore these variations below.
Type 1: Classic Trigeminal Neuralgia
Also known as “classic,” Type 1 trigeminal neuralgia is the most common form. If you have this condition, you’ll experience episodes of sharp and burning sensations on one side of your face.
These episodes start with mild numbness and tingling and reach full intensity within seconds. Each burst of pain can last from a few seconds to two minutes before subsiding.
The bouts of pain usually occur in close succession and are followed by brief pain-free periods. They can continue intermittently for up to two hours, with some people experiencing hundreds of attacks a day. After a flare-up, you may enjoy a period of remission without pain for months or years. However, the remission periods tend to shorten over time, and the pain inevitably returns.
A flare-up of trigeminal neuralgia can be triggered by contact with the cheek, vibration, or touch, such as when washing your face, eating, or drinking. Attacks rarely occur during sleep.
Type 2: Atypical Trigeminal Neuralgia
Atypical, or Type 2, trigeminal neuralgia is less common than classic TN. This form causes painful sensations that may be less intense but more widespread and constant. People with atypical TN often describe their pain as stabbing, burning, aching, or dull, and they generally have more difficulty managing their symptoms.
While Type 2 TN pain may not be as excruciating as Type 1, it can be equally life-limiting, especially as attacks progress and worsen over time. Additionally, the periods of remission become fewer and shorter, and medications become less effective in controlling the pain.
Complicating the clinical picture of Type 2 trigeminal neuralgia is the overlap of symptoms with other conditions, such as temporomandibular joint (TMJ) disorders, craniocervical instability (CCI), and transverse cervical nerve (TCN) disorders. This often leads to misdiagnosis and inadequate treatment.
Characteristics Of Trigeminal Neuralgia Pain
Trigeminal neuralgia pain can vary among individuals, but there are common patterns. The pain is known to be one of the most excruciating sensations, often described as worse than childbirth or a heart attack.
Additionally, the attacks typically follow a similar pattern:
- During an attack, shock-like sensations occur in rapid succession, each lasting between a few seconds and two minutes.
- Intermittent bouts of pain can last for two hours or longer. As the damage to the trigeminal nerve progresses, attacks tend to last longer and become more intense.
- Periods of remission can last from a few weeks to several years. However, trigeminal neuralgia never disappears on its own, and the pain-free periods tend to shorten over time.
- Trigeminal neuralgia pain typically affects one side of the face. In nearly 60% of cases, the right side of the face is affected. Bilateral neuralgia is very rare.
Working with a specialist can help you better understand the patterns and characteristics of trigeminal neuralgia pain.
Recognizing the Signs of Facial Nerve Disorders
Although pain is the most prominent symptom of trigeminal neuralgia, the painful sensations caused by this condition can vary from person to person. If you have TN, here are some of the most common symptoms you might experience:
- Sudden, Severe, Electric Shock-Like or Stabbing Pain: A damaged trigeminal nerve tends to misfire and send inappropriate pain signals to the brain, resulting in electric shock-like sensations on one side of the face.
- Pain Felt on One Side of the Face: In trigeminal neuralgia, the pain will be localized to the side of the face where nerve damage or irritation occurred. If a specific branch of the trigeminal nerve is affected, you may experience pain in the upper, middle, or lower portion of the face. Damage to the mandibular (lower) branch of the trigeminal nerve is the most common form of TN.
- Pain Triggered by Actions Such as Chewing, Talking, or Brushing Teeth: Nerve damage can cause painful sensations in response to stimuli that are normally painless. In trigeminal neuralgia, an irritated trigeminal nerve can react to mild sensations, such as brushing your teeth, shaving, applying makeup, or even touching your lip with your tongue.
- Pain That Occurs in Bursts or Episodes: Especially if you have Type 1 trigeminal neuralgia, the painful sensations will be concentrated in intense, intermittent bursts of pain.
- Intense, Sharp, or Shooting Pain: Whether you have Type 1 or Type 2 trigeminal neuralgia, the pain will manifest as intense, sharp, stabbing, or shooting sensations. Over time, these painful sensations can last for up to 2 minutes before subsiding.
- Pain That Spreads to Other Areas of the Face: Painful sensations are often concentrated on one side of the face, depending on which trigeminal nerve or branch has been damaged. Trigeminal neuralgia can also occur on both sides of the face, and the pain can spread to your eyes, mouth, nose, scalp, and forehead.
- Pain Accompanied by Involuntary Twitching, Grimacing, or Wincing of the Face or Mouth: Damage to the trigeminal nerve can also affect motor signals traveling to the brain, which are related to muscle movement. This can cause involuntary muscle movements such as twitches, spasms, and cramps.
- Numbness or Weakness: Although trigeminal neuralgia is primarily characterized by pain, nerve damage can also prevent pain and touch signals from reaching the brain. When this happens, you may experience numbness or weakness in several parts of your face.
Neuralgia
The nerves throughout our bodies enable muscle movement, control essential functions, and process touch and temperature sensations. Ultimately, they play a vital role in helping us experience the world around...
Neck Pain
Neck pain is a common issue that can affect people of all ages. The neck is a complex structure consisting of the spine, spinal cord, and various supporting muscles, ligaments, and tendons. Given its intricate nature, it's understandable that there are...
Common Causes of Facial Nerve Issues
Trigeminal neuralgia is a condition resulting from the abnormal functioning of the trigeminal nerve. This dysfunction can occur due to nerve damage, irritation, or compression, but it can also be idiopathic (without a known cause) in some cases.
Below are some common triggers of trigeminal neuralgia:
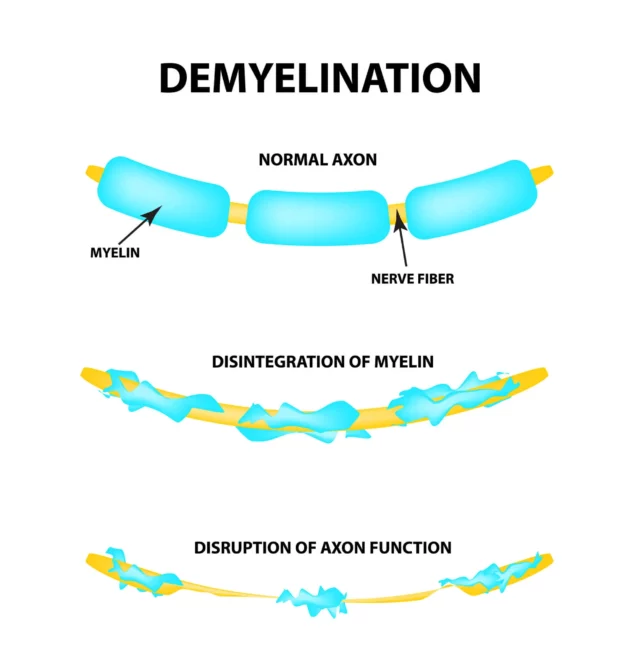
- Compression of the Trigeminal Nerve: The trigeminal nerve often becomes compressed when a nearby blood vessel—either an artery or vein—comes into contact with the nerve. This contact presses on and irritates the nerve, damaging the myelin (the nerve’s protective sheath). Vascular compression is the most common cause of trigeminal neuralgia, but pressure on the trigeminal nerve can also be caused by abnormalities such as a tumor.
- Multiple Sclerosis: Other conditions, such as multiple sclerosis (MS), can cause demyelination (damage to the myelin) of the trigeminal nerve. Studies have shown that 15% of people affected by trigeminal neuralgia are later diagnosed with MS, while up to 3.4% of people with multiple sclerosis experience TN.
- Injury or Trauma: Surgical injury (often following oral or sinus surgery) or facial trauma can damage the trigeminal nerve, leading to TN. The symptoms of TN caused by injury or trauma are similar to those caused by dental problems, and people with undiagnosed trigeminal neuralgia often undergo several dental procedures to attempt to address the pain.
- Genetics: In 1-2% of trigeminal neuralgia cases, there are inherited or genetic factors. Although the relationship between genetics and TN is not fully understood, having a family member with this condition may increase your risk of developing it.
- Other Medical Conditions: Conditions such as stroke and brain lesions may damage the trigeminal nerve or lead to pain similar to that caused by trigeminal neuralgia. New research is also exploring whether nerve damage caused by shingles may be related to trigeminal neuralgia.
After the onset of symptoms, trigeminal neuralgia becomes a lifelong, chronic condition. Although you may experience pain-free periods of remission, new attacks can be triggered by various factors, including:
- Experiencing a light breeze or gust of wind on your face
- Touching your face
- Eating or drinking
- Talking or smiling
- Brushing your teeth or touching your teeth with your lips
- Pressing on your cheek or jawline
These triggers may change over time. However, understanding what triggered previous attacks may help you prolong periods of remission.
Factors Contributing to Facial Nerve Pain
Although anyone can experience trigeminal neuralgia, certain factors may increase your risk:
- Age: The aging process can lead to a decline in the health and function of the nervous system, making trigeminal neuralgia and nerve damage more likely. This condition mostly develops in adults between 37 and 67 years old.
- Gender: Women are twice as likely as men to suffer from TN.
- Excessive Dental Procedures: Invasive or improper dental procedures can damage the trigeminal nerve.
- Cardiovascular Disease: If you have high blood pressure or have suffered a stroke, the trigeminal nerve is more likely to be compressed by a blood vessel or damaged.
- Playing Contact Sports: Engaging in activities that increase the chances of facial trauma can increase your risk of developing trigeminal neuralgia later in life.
Evaluating Facial Nerve Disorders
Although there is no definitive diagnostic procedure for trigeminal neuralgia, a neurologist or healthcare specialist can determine the cause of your facial pain. However, because symptoms often overlap with other conditions, atypical TN is more challenging to identify and can sometimes be misdiagnosed.
Diagnosing trigeminal neuralgia involves the following steps:
- Medical History and Physical Examination: Your doctor will review the nature and pattern of your symptoms, assess your medical history, and perform a physical examination of your face to rule out other underlying conditions.
- Neurological Examination: During a neurological exam, a specialist will evaluate your mental health, muscle strength, and reflexes. They will also check for nerve abnormalities by testing facial sensations, checking your hearing and vision, and observing the movement of your eyes, mouth, neck, and shoulders.
- Imaging Studies: Computerized tomography (CT) and high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans provide a clear picture of the anatomy of the trigeminal nerve. These scans can identify abnormalities such as a tumor or blood vessels that may be compressing the nerve. These tests can also diagnose underlying conditions causing trigeminal neuralgia pain, such as multiple sclerosis.
- Electrophysiological Tests: These tests are used to evaluate the health of your body’s electrical system.
Common Treatment Options
As seen above, trigeminal neuralgia is a lifelong condition with no definitive cure. However, healthcare professionals can prescribe several treatment options to ease the intensity of the pain, reduce the frequency of attacks, and prolong periods of remission.
Prescription Medications
Commonly prescribed medications for TN include:
- Anti-seizure Medications: Antiepileptic drugs may interfere with the transmission of pain signals sent by damaged or overly sensitized nerves, such as in the case of an irritated trigeminal nerve. This class of pharmaceuticals is more effective for Type 1 trigeminal neuralgia than for Type 2.
- Antidepressants: These medications work by stimulating the activity of neurotransmitters in the spinal cord, which are responsible for reducing and modulating pain signals.
- Nerve Blocks: These are injections of steroid medications that provide temporary relief from pain.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery
If medications have not provided the desired results, your doctor may suggest a surgical procedure called stereotactic radiosurgery. This type of surgery uses a tool known as Gamma Knife or CyberKnife to create a lesion at the root of the trigeminal nerve using a concentrated amount of focused radiation.
This procedure severs the connection between the trigeminal nerve and the brain, thus stopping the sensation of pain. This intervention can relieve trigeminal neuralgia pain for up to three years but may worsen sensations of numbness and weakness in the face.
When choosing a pharmacological treatment, it is important to remember that trigeminal neuralgia is a progressive and chronic condition. This means you may need to take medications daily for years, and their efficacy may decrease over time. This can expose you to severe side effects, including the risk of addiction.
Percutaneous Procedures
Percutaneous, or “through the skin,” surgical procedures are used to destroy some nerve fibers in the trigeminal nerve. This can reduce pain for two years or longer.
These procedures are known as rhizotomy. Several types of rhizotomy can be used for trigeminal neuralgia, including:
- Balloon Compression: A small tube is inserted through the cheek and guided to the trigeminal nerve. A catheter with a small balloon is then inflated, causing pressure that damages the nerve fibers causing pain.
- Glycerol Injection: A small amount of sterile glycerol is inserted into the area of the trigeminal nerve where it splits into three branches. This substance selectively damages the nerve to relieve painful sensations.
- Radiofrequency Thermal Lesioning: This procedure selectively damages the area of the trigeminal nerve causing pain by briefly heating the nerve to 80°C.
Another surgical procedure used to treat trigeminal neuralgia is microvascular decompression. In this procedure, the blood vessels compressing the trigeminal nerve are removed or relocated. This is the most invasive surgical option for TN.
Alternative Therapies
According to a 2021 study, alternative and complementary therapies, when coupled with other treatments, can be beneficial in relieving TN pain and easing the intensity of attacks. Some of these therapies include yoga, meditation, biofeedback, aromatherapy, acupuncture, low-impact exercise, and creative visualization. These approaches help relieve stress and trigger the production of pain-relieving hormones, such as endorphins.
The NextPain Care Approach for Trigeminal Neuralgia
Living with trigeminal neuralgia can be incredibly challenging, but it doesn’t mean you have to endure constant pain. At NextPain Care, we offer a comprehensive and empathetic approach to managing your condition, aiming to alleviate pain and enhance your quality of life.
With NextPain Care’s proprietary whole-person methodology, we address all aspects that may be contributing to your condition. Our 3-level comprehensive approach includes a range of treatment options, starting with conservative therapies, progressing to medications, and utilizing advanced procedures if necessary. This ensures personalized care designed to help you find relief and return to enjoying your life.
Explore the treatment options below to learn more about how we can support your journey to pain management.
Nerve Block
Nerve blocks involve the injection of medication to interrupt pain signals from specific nerves. NextPain Care uses nerve blocks to provide targeted pain relief for various conditions, including chronic pain and acute post-surgical pain. This minimally...
Radiofrequency Ablation
Radiofrequency ablation is a procedure that uses heat to disable nerves responsible for transmitting pain signals. At NextPain Care, this minimally invasive treatment is utilized to address chronic pain conditions, particularly in the spine. NextPain Care's...
"Treatment options are tailored to your individual needs, and availability may vary based on factors such as location and insurance. We’re here to guide you through the possibilities and help determine the best course of action for your journey to relief and recovery."
Managing Trigeminal Neuralgia With NextPain Care
At NextPain Care, we are dedicated to helping you manage the debilitating pain of trigeminal neuralgia with a comprehensive, patient-focused approach. Our expert team uses the latest advancements in medical treatments and personalized care plans to meet your unique needs.
Don’t let trigeminal neuralgia control your life any longer. Trust NextPain Care to be your partner in this journey, offering compassionate care and effective solutions. Take the first step towards reclaiming your comfort and well-being—reach out to us today and learn how our treatments can help improve your quality of life.
Our Providers
We take great pride in the wealth of talent and expertise that our providers have as they improve the health outcomes of our patients, each and every day.
It's time to take control and find relief.